Smart Prosthesis Control
Enhancing Usability and Autonomy
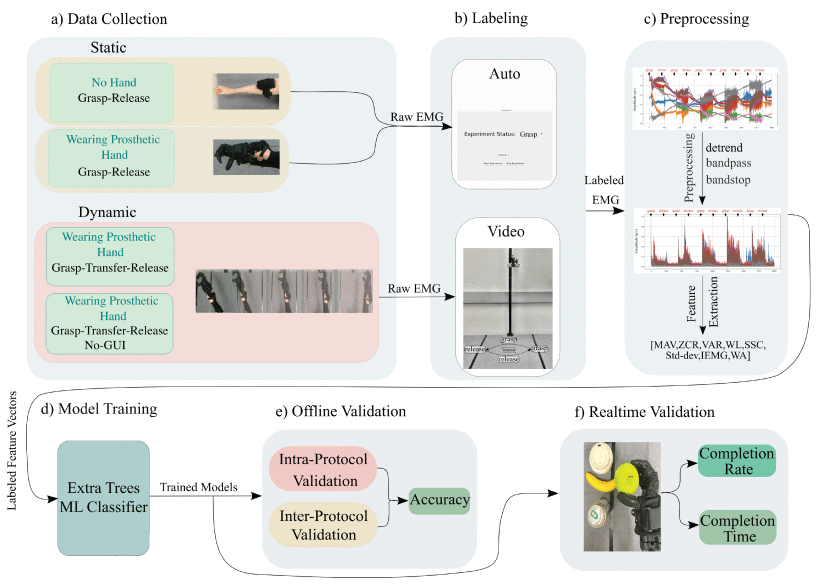
Our work in smart prosthetic control focuses on developing systems that are more intuitive, robust, and less cognitively demanding than traditional myoelectric interfaces. A significant effort has been made toward achieving biosignals-free autonomous control for prosthetic hands, utilizing imitation learning from human demonstrations and vision-only systems to handle grasping and releasing objects of various shapes and weights (Shi et al., 2025). This method aims to provide users with a very easy-to-use interface that substantially reduces mental fatigue.
In parallel, we have investigated methods to improve the robustness and accuracy of classic myoelectric pattern recognition (MPR). Research has focused on the impact of various training protocols on MPR control in upper-limb prostheses, showing that incorporating the weight of the prosthetic hand and dynamic arm movements into the training data improves both accuracy and robustness, especially for amputee participants (Mohammadreza et al., 2025).
To further boost performance, we explored multimodal integration, combining sEMG signals with computer vision. We identified a “sweet period” during the early reaching phase where visual data could accurately classify grasp patterns, which, when integrated with sEMG data from the grasp phase, significantly improved overall grasp classification accuracy (Wang et al., 2022). This foundational work is crucial for developing robust, real-time control systems for multi-degree-of-freedom prostheses.
Overall, our research aims to simplify the user experience, moving toward systems that intelligently assist the user and restore a more natural level of functional independence.
References
2025
-
Investigating the Impact of Training Protocols on Myoelectric Pattern Recognition Control in Upper-Limb AmputeesIEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2025
-
Towards Biosignals-Free Autonomous Prosthetic Hand Control via Imitation LearningIEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2025
2022
-
Integrating computer vision to prosthetic hand control with sEMG: Preliminary results in grasp classificationFrontiers in Robotics and AI, 2022